Epsilon Indi
Epsilon Indi
Fact
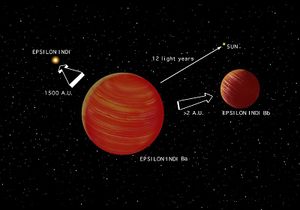
Epsilon Indi (ε Indi, ε Ind) is a star system approximately 12 light-years from Earth in the constellation of Indus consisting of a K-type main-sequence star, ε Indi A, and two brown dwarfs, ε Indi Ba and ε Indi Bb, in a wide orbit around it. The brown dwarfs were discovered in 2003. ε Indi Ba is an early T dwarf (T1) and ε Indi Bb a late T dwarf (T6) separated by 0.6 arcseconds, with a projected distance of 1460 AU from their primary star.
Estimates provided by the NASA Star and Exoplanet Database indicate that the inner edge of Epsilon Indi's habitable zone could be located around 0.411 AU from the star, while the outer edge edge lies around 0.810 AUs. The distance from the star where an Earth-type planet could have liquid water on its surface is centered around 0.611 AU -- between the orbital distances of Mercury and Venus in our Solar System. At that distance from Epsilon Indi and assuming that it has 0.77 Solar-mass, such a planet would have an orbital period of around 199 days (or a bit over half an Earth year).
The brown dwarfs are likely far enough away from the primary to have negligible effect on any planets in the habitable zone. Their distance from the star is almost 50 times further than Pluto's average distance from our sun. (Indeed, our own Solar System could have an undiscovered brown dwarf at that distance.)
Fiction
Epsilon Indi is the primary star of the planet Taprobane (Epsilon Eridani III), home of the Timoans.